Types of Cyber Attacks to Expect in 2024:
Insights from the SonicWall Cyber Threat Report
In today’s interconnected world, where digital transformation is rapidly evolving, cyber threats continue to pose a significant risk to businesses of all sizes. The SonicWall Cyber Threat Report for 2024 sheds light on the evolving landscape of cyber attacks, offering valuable insights into the types of threats organizations can expect to face in the coming year. Let’s delve into some of the key takeaways from the report and explore the potential types of cyber attacks on the horizon.
The Target: Small Businesses
Contrary to popular belief, small businesses are not immune to cyber threats; in fact, they are three times more likely to be targeted than larger organizations. SonicWall’s commitment to researching and publishing the latest threat intelligence is crucial, especially considering that small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) make up 80% of their end users.
Trends from 2023
The year 2023 witnessed a significant acceleration in cyber threats, with an 11% year-over-year increase in malware attacks. Encrypted threats rose by a staggering 117%, while cryptojacking experienced an alarming 659% surge. Despite the overall increase in attack volumes, the report highlights a decline in never-before-seen malware detections by 38%. This data implies that attackers are sticking to their traditional methods and constantly improving those instead of creating new never-before-seen malware.
Malware Landscape
Malware attacks reached a global volume of 6.06 billion in 2023, marking the highest since 2019. While Asia and Europe experienced a decrease in malware, North America and LATAM saw increases of 15% and 30%, respectively. Interestingly, malicious OneNote files emerged as a popular initial threat vector, showcasing threat actors’ adaptability.
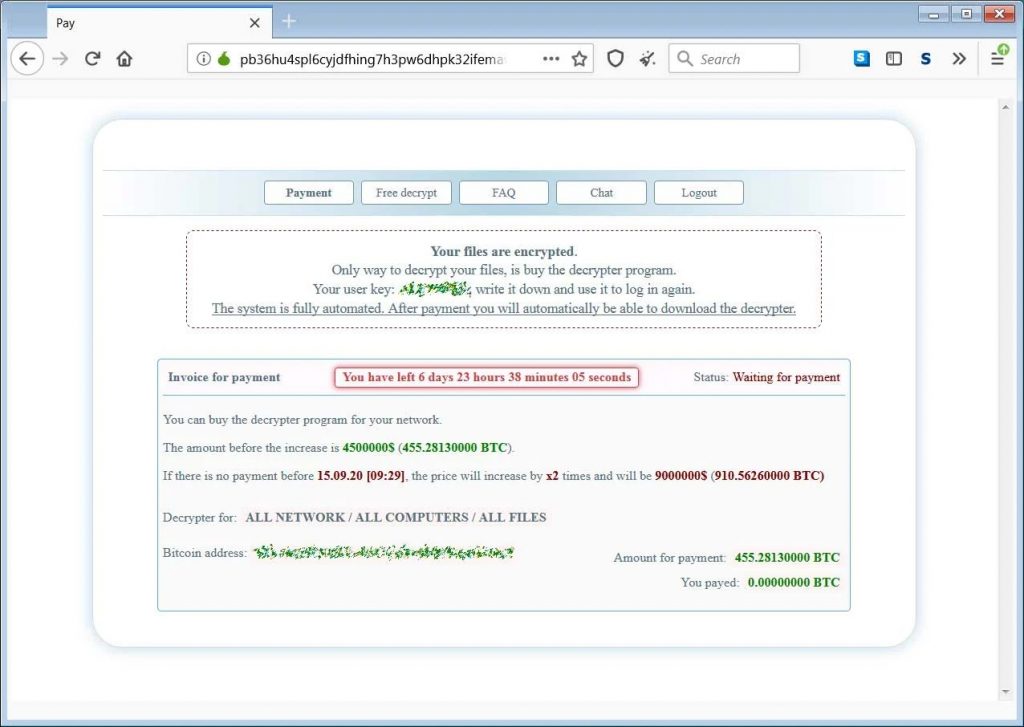
Ransomware Resilience
Ransomware attacks totaled 317.6 million, indicating a 36% decrease year-over-year. Despite this decline, Asia witnessed a record high in ransomware volumes, rising by a staggering 1,627% since 2019. LockBit remained a formidable ransomware group, showcasing consistent innovation with bug bounty programs and regular toolkit updates. Threat actors aren’t slowing down, but for the time being, they’re finding variants that work and using them repeatedly.
Intrusion Attempts on the Rise
Intrusion attempts continued to climb, reaching 7.6 trillion in 2023, a 20% increase over the previous year. Malicious intrusion volumes rose across various industries, contributing to alert fatigue and potential data breaches.
Encrypted Threats Surge
Encrypted attacks more than doubled in 2023, reaching 15.7 million. While North America saw a 30% increase, Europe, Asia, and LATAM experienced triple-digit spikes. Industries such as healthcare, education, government, and retail witnessed significant encrypted threat surges.
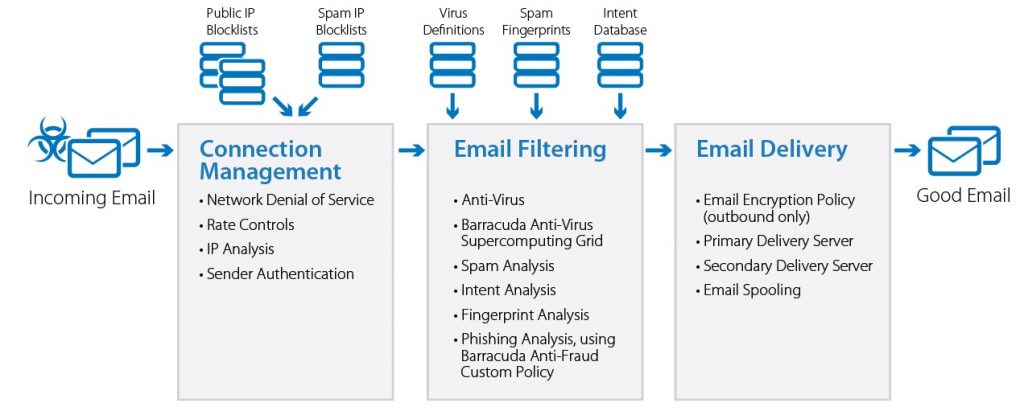
Attackers are using encryption protocols more frequently to hide malware, ransomware, zero-day attacks and more. Older generation firewalls and other traditional security controls lack the capability to detect, inspect and mitigate threats sent over HTTPs traffic. This means the older the hardware and software you have, the easier it is for attackers to deploy and execute attacks on your business. If you have outdated firewalls or software, take a look at SonicWall’s Gen 7 Firewalls and other licensing here. There are affordable options for any size business that will protect you from these types of cyber attacks.
Cryptojacking’s Unprecedented Growth
Cryptojacking hits skyrocketed by 659% in 2023, reaching 1.06 billion. XMRig, a legitimate tool often abused by threat actors, remained a prevalent choice for cryptojacking attacks. The environmental and financial costs associated with crypto mining underline the seriousness of this growing threat.
Looking Ahead to 2024
As threat actors continue to adopt advanced technologies, the future threat landscape is expected to evolve rapidly. The use of AI in refining phishing attempts, executing convincing Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, and generating malicious code poses new challenges for defenders.
Recommendations for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- Enable Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Strengthen authentication security by implementing MFA to prevent unauthorized access.
- Patch Promptly: Stay vigilant in applying patches promptly, as most exploit attempts target vulnerabilities that may have been known for months or years.
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and fortify defenses through regular security assessments.
- Ongoing Security Training: Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices to build a vigilant and informed workforce.
- Scan Encrypted Traffic: Given the rise in encrypted attacks, ensure that all network traffic, especially encrypted traffic, is regularly scanned for potential threats.
- Extend Protection to the Cloud: With the increasing adoption of cloud services, implement comprehensive security measures such as Security Service Edge (SSE) and Zero-Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA).
- Update Security Appliances and Software: Legacy firewalls and software do not detect or mitigate threats as well as new generation products. Secure your business with updated firewalls now.
In conclusion, the SonicWall Cyber Threat Report for 2024 highlights the persistent and evolving nature of all types of cyber threats. By staying informed and implementing robust cybersecurity measures, businesses can enhance their resilience against the ever-changing threat landscape.
Unsure About Your Network Security?
If you’re unsure about the security measures you have in place, our team can assess what you currently have and help patch any holes. Give us a call or send us an email and we would be happy to help.
You can also browse the newest SonicWall products that are sure to detect and mitigate all types of cyber attacks that threaten your business.